Canada is home to some of the brightest scientific minds in the world. Home to renowned research universities and a government that continues to believe in funding world-changing projects, Canada is known on the world stage for its scientific contributions throughout the country’s relatively short history.
What does it take to be a great science innovator? A love for problem solving, a desire to help others, resilience, drive - just to name a few key traits. Add a solid foundation of knowledge in areas like chemistry, biology, engineering, or medicine, and you are well equipped to make world-changing discoveries.
Aspiring scientists can look no further to the examples of Canadian-made inventions such as insulin, pablum, the Canadarm, or the unique research facilities of the Experimental Lakes Area to gain inspiration. The work of Banting and Best, Tisdall and Drake, Anthony Zubryzcki, and David Schindler continue to influence scientists today.

This article is all about some of the most famous inventions and research in Canadian history and the scientists behind the work. Anyone looking to learn more about the work of Canadian scientists will be inspired by the year of collaboration and problem-solving required to develop these innovations.

How did Insulin Change the World?
Diabetes is a medical condition that impacts millions around the world. Prior to the discovery of insulin, any diagnosis of diabetes was devastating - a far cry from the millions that thrive with diabetes today.
The discovery of insulin by Canadian doctor Frederick Banting completely changed the treatment of diabetes. Through the manufacturing of insulin, diabetes was no longer a fatal disease, becoming a manageable chronic condition.
Insulin is a naturally occurring hormone that is made by the pancreas. It enables your body to use glucose, or sugar, for energy. Without enough insulin, high blood sugar levels in the body are reached, resulting in diabetes.
Prior to the invention of insulin, treatments for type 1 diabetes were limited to starvation diets that often resulted in complications like malnutrition and death. Until the early 20th century, diabetes was mysterious and not understood by health professionals.
Who Invented Insulin?
The invention insulin was driven by brilliant scientific inquiry, with Canadian Frederick Grant Banting at the centre of its development. Born in 1891 in Alliston, Ontario, Banting was a medical doctor who served in World War I.
Banting studied the work of Moses Barron, who suggested a link between pancreatic islets and diabetes. Banting put forth the hypothesis that isolating the release of pancreatic islets could solve the mystery of treating diabetes.
Through collaborating with Dr. John Macleod, research assistant Charles Best, and James Collip, Banting discovered a way to treat diabetes successfully.
How was Insulin Discovered?
Here are some key moments in the discovery of insulin.
1920
MacLeod provides Banting with support.
Dr. John Macleod, a University of Toronto professor and expert in carbohydrate metabolism, provides Banting with lab space, funding, and a research assistant named Charles Best.
May 1921
Experiments Begin.
Banting and Best start experimentation using the pancreatic ducts of dogs. They develop an early form of insulin using materials extracted from the animals.
July 1921
James Collip joins the team.
Banting and Best inject their extract into a dog with diabetes. The dog’s sugar levels drop dramatically. The results of the trial indicate they are making progress, though some test subjects react adversely because their initial extract requires refinement. To develop a purer extract, Dr. Macleod calls biochemist James Collip, who has the expertise to develop a better insulin extract for human trials.
January 1922
Insulin is tested on Leonard Thompson.
Insulin is tested on Leonard Thompson, a 14 year old boy with a severe case of diabetes. Initially, the injection is only partially successful. With improvement to the extract, Thompson’s blood sugar levels drop his condition is improves. News of spreads rapidly:the medical community sees the potential of insulin to save lives.
End of 1922
Insulin is produced commercially.
Insulin is produced commercially, and is made available to diabetics worldwide.
How is Insulin Manufactured?
Following Banting pharmaceutical companies in the early 20th century commercially produced insulin by extracting and purifying the insulin found in the pancreases of pigs and cattle. Early insulins varied greatly in purity and effectiveness.
As purification techniques improved, the quality of insulin improved. Though not identical to human insulin, animal-based insulin was highly effective.
Progress in biotechnology provided an alternative source to animal insulin. Recombinant DNA, a scientific technique developed in the 1970s, enabled pharmaceutical companies to engineer bacteria to create human insulin. The first “recombinant insulin” was known as “Humulin”.
Banting and Best's discovery of insulin continues to be recognized and celebrated by Canadians and health professionals around the world.
The Development of Pablum by Frederick Tisdall and Theodore Drake
Infant nutrition is an essential foundation for society - healthy babies become healthy children and adults. Nutritional gaps and deficiencies in the earliest moments of human life can result in death or long-lasting impacts to health.
For this reason, the invention of pablum by Frederick Tisdall and Theodore Drake is a key moment in Canadian medical history. Through their invention of a fortified infant cereal, Tisdall and Drake made a major impact on infant mortality in Canada and around the world.
Pablum is a nutritious, pre-cooked, digestible multi-grain cereal for infants. The cereal was meant to be mixed with breast milk or formula to create a smooth and easy-to-digest food for babies. The word “pablum” comes from the Latin word “pabulum”, which means food.
Why was the Discovery of Pablum Important?
- From the 1920s-1940s, Canada had high rates of infant mortality, largely as a result of malnutrition and diseases caused by contaminated and unpasteurized cows’ milk.
- Mothers typically developed their own homemade formulas and cereals, usually from soaked biscuits.
- However, these homemade formulas did not have the adequate nutrients to prevent childhood illnesses including rickets, a disease that softened the bones of children.
- These foods also upset the sensitive gastrointestinal tracts of infants, causing diarrhea and other issues.
Who Invented Pablum?

The Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto saw the need to meet the nutritional needs of infants, and assembled a team of doctors and nutritionists.
In 1918, the Nutritional Research Laboratories (NRL) was opened. The team included Dr. Alan Brown, the chief of paediatric research, Dr. Frederick Tisdall, Dr. Theodore Drake, and nutritionist Ruth Herbert. Each brought expertise in paediatrics, nutrition, and biochemistry.
Though Tisdall made great advances in the area of child nutrition, it is important to note his reputation has been tarnished due to his involvement with unethical and harmful experimentation on Indigenous children in Canada.
Left: a photo of Frederick Tisdall (Source: Wikimedia).
How was Pablum Invented?
Tisdall led the NRL to research and develop nutritious foods and products that contained essential vitamins. They started by developing the Sunwheat Biscuit in 1930, a biscuit for children containing vitamins and minerals.
They then worked to develop an infant-targeted solution by creating a cereal similarly rich in minerals, vitamins, and protein that would not cause digestive problems. The cereal’s ingredients included:
- Whole wheat meal
- Oatmeal
- Corn meal
- Wheat germ
- Bone meal
- Brewer’s yeast
- Alfalfa
- Salt
The recipe was fortified with calcium phosphorous, iron, copper, and five vitamins. Early versions, however, required long cooking times.
The Breakthrough
Tisdall and his team eventually learned of a new process to dehydrate milk with a heated drum, and used similar techniques to produce the cereal. The formula was cooked in a large pressurized steam kettle, dried on the rotating drum, and scraped off.
What resulted was a dry, flaky powder that maintained all the nutrients. Mothers could easily and quickly mix the cereal with milk or water, and serve it to babies.
Pablum continues to shine as a nutritious and easy-to-prepare food for infants - a product needed for new mothers.
Why is David Schindler’s Research in Environmental Chemistry so Important?
Humans have made detrimental impacts on the world’s water systems over the last few hundred years, as we continue to exploit natural resources for capital gain. David Schindler, an American-Canadian ecologist and environmental scientist, advocated and protected aquatic environments through his groundbreaking research.

His research on the impact of human activities on freshwater systems has shaped and informed environmental policy and conservation work.

Who Was David Schindler?
David Schindler was born in Fargo, North Dakota in 1940 and grew up in Northern Minnesota. He earned a bachelor’s degree in zoology in 1960 from North Dakota State University.
An academically and athletically gifted student, Schindler attended the prestigious Oxford University on a Rhodes Scholarship where he studied and earned his PhD in the company other renowned scientists like Nobel Laureate Nikko Tinbergen.
Schindler surprisingly turned down job offers from schools like Yale and the University of Michigan to work at Trent University in Peterborough, Ontario - a lakeside town similar to the one he had growing up in.
In 1968, he worked with the Freshwater Institute at the University of Manitoba (FWI). He founded the Experimental Lakes Area research program in Northwestern Ontario. In 1989, he became a chair at the University of Alberta’s faculty of Science.
What was Schindler’s Impact on Environmental Chemistry?
Schindler’s most significant impacts came during his work at the Experimental Lakes Area (ELA) in Ontario.
The ELA is a research facility of 58 small lakes: a unique context that enables scientists to conduct whole lake experiments in natural conditions. The ELA is the only place in the world scientists can implement long term projects and experiments to understand what human activity can do to the earth’s freshwater.
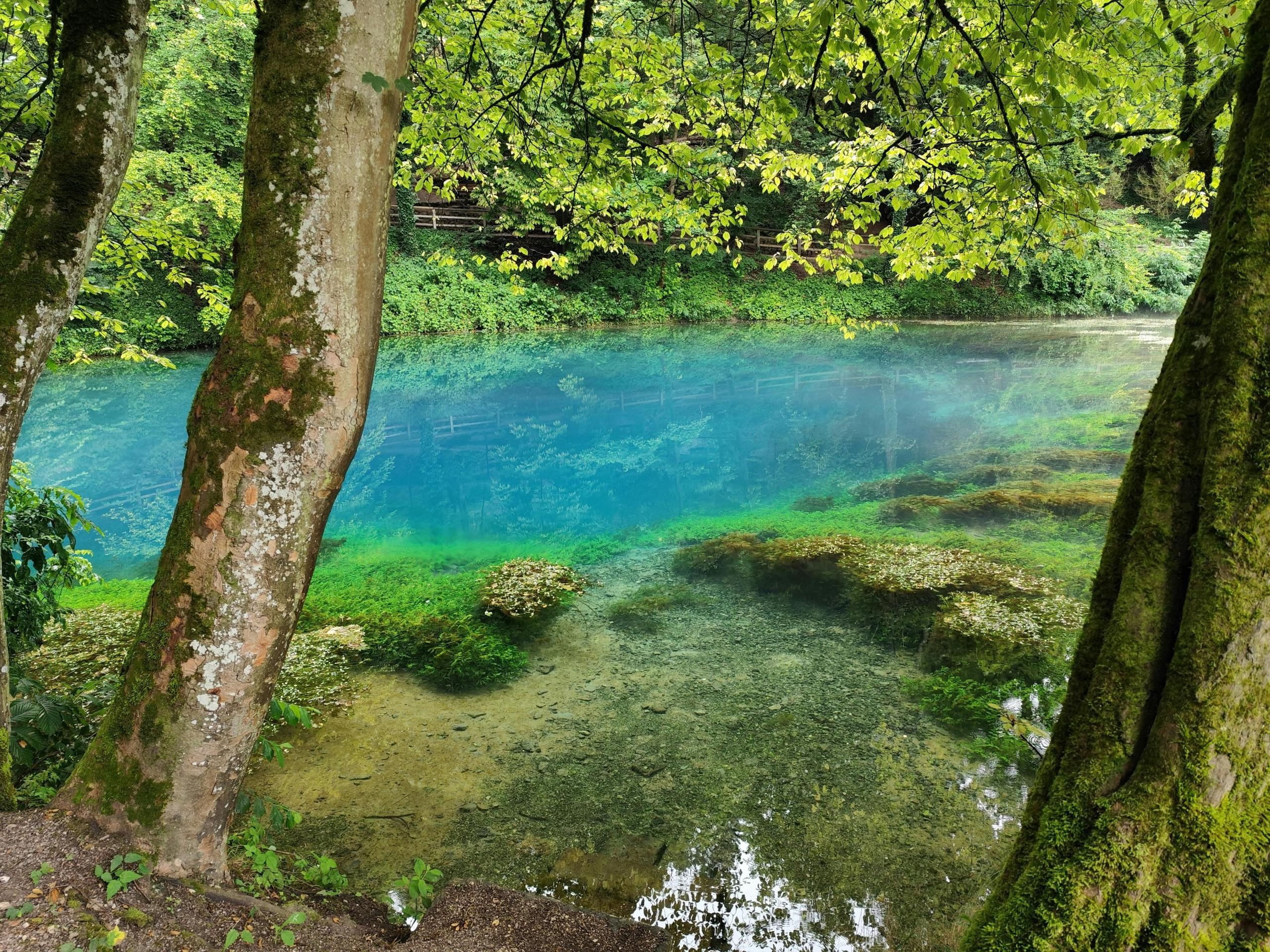

Schindler’s Critical Research on Phosphorous and Eutrophication in Freshwater
Schindler’s landmark study at the Experimental Lakes Area demonstrated the role of phosphorous in causing overgrowth of algae and oxygen depletion in bodies of water (eutrophication).
Schindler and other scientists divided a lake with a plastic curtain and added different nutrients on each side. The experiment showed that phosphorous was the primary driver of algae growth.
Their research lead to ban of phosphorous in detergents and fertilizers - a major policy shift that lowered eutrophication around the world.
Acid Rain and Mercury Research
Schindler researched acid rain, an environmental issue in the 1970s and 1980s.
He acidified the lakes at the ELA, and showed the harmful impacts of acid rain on aquatic ecosystems such as the decline of fish populations and changes to water chemistry. His work provided evidence that lead to agreements like the Canada-U.S. Air quality agreement to reduce sulphur dioxide emissions.
Schindler’s work also extended to mercury contamination in freshwater ecosystems.
ELA research showed how mercury from industry accumulates in the aquatic food chain and the health risks to wildlife and humans. Their findings informed the global understanding of mercury and was used to develop regulations aimed at lowering mercury emissions to protect wildlife.
Schindler’s Awards and Recognition
Schindler’s research was highly influential and was awarded the following awards:
- Stockholm Water Prize
- Tyler Prize for Environmental Achievement
- Gerhard Herzberg Canada Gold Medal for Science and Engineering
- Fellow, Royal Society
David Schindler's work has been critical as humans strive to become better stewards of planet earth and its precious waters.
Canadian Robotics Innovation in Space: the Canadarm
The Canadarm, officially known as the “Shuttle Remote Manipulator System” (SRMS), is a robotic arm that can perform delicate operations and manoeuvres in space. It was developed in the 1970s for NASA’s Space Shuttle program.
The Canadarm, one of the most iconic symbols of engineering and robotics, is one example of genius innovation from a relatively lesser known Canadian, Anthony Zubryzcki. His creation was a crucial tool used for over 30 years by NASA.
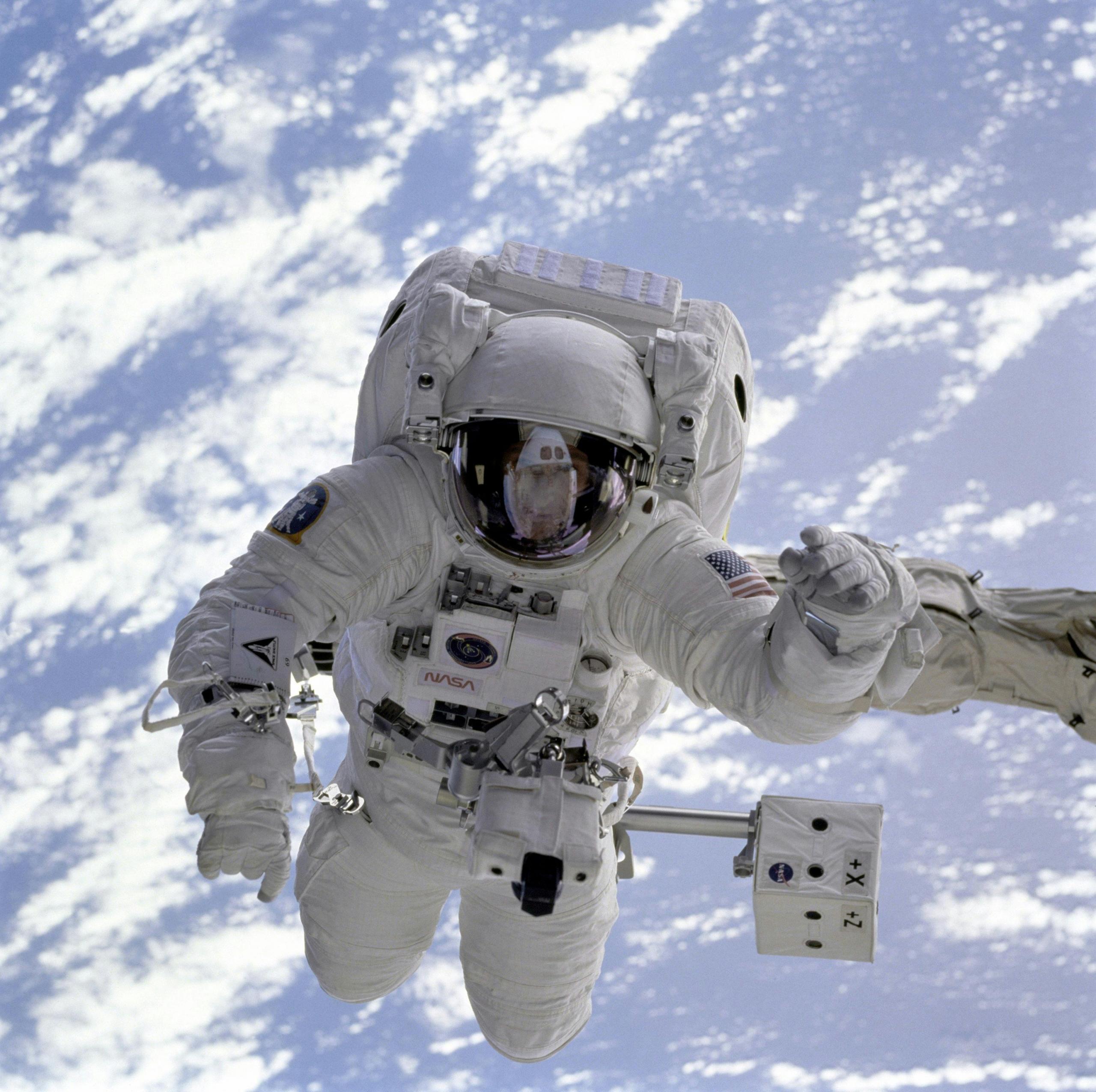

Who Invented the Canadarm?
Anthony “Tony” Zubryzycki was an Polish-Canadian engineer passionate about innovation and problem-solving. With expertise in robotics and mechanics, he was an ideal leader for the project. He understood the complexities of robotics and the need to create something sophisticated and strong enough to withstand the extreme conditions of space.
With a team, he spent years developing the Canadarm, continually iterating the design after feedback and testing, ensuring it met NASA’s stringent requirements.
The Canadarm made its debut on November 13, 1981 on the second flight of the Space Shuttle program (STS-2).
What is the Canadarm?
The Canadarm performed difficult tasks like deploying satellites, servicing shuttles, and helping astronauts during extravehicular activities. The arm can maneuver heavy objects, perform repairs, and retrieve objects in space with precision. Canadarm even helped to repair the Hubble Space Telescope. It was used over the course of 30 years in over 90 missions.
The arm has multiple joints that allow it to move with a high degree of freedom, mimicking the motion of a human arm. Each joint had precision motors and sensors to enable it to perform complex movements accurately. Modern materials like carbon composite was used for its lightweight and durability.
Why Was Canada Chosen by NASA to build the Canadarm?
NASA invited the Canadian government to participate in the 1969 space shuttle program to recruit international talent. Initially, NASA considered requesting Canada to build a tool for deploying satellites, but became interested in a robot invention instead.
In 1974 NASA awarded Canada the contract to design a Shuttle Remote Manipulator System and an associated simulator facility. Canada had no space agency at the time, so the National Research Council of Canada coordinated a team led by SPAR Aerospace.
The Canadarm is remembered fondly by Canadians and space enthusiasts as a game-changing robot that advanced exploration of the "final frontier."
How Can I Pursue a Career in Scientific Research?
If you are inspired by the stories of great Canadian scientists, you may be wondering how you can be part of this tradition of research and innovation.
Perhaps your passion is in finding a solution for a disease or ailment; maybe you are motivated to prevent the collapse of the environment from human activity; or it could be developing robotic solutions that gets you excited. Whatever your motivation is, you can certainly find a learning and career pathway that is right for you.
Leading Canadian research universities like the University of Toronto and the University of British Columbia have faculty with a wealth of experience and knowledge. They work directly with hospitals, laboratories, and innovation hubs to develop solutions that are implemented in Canada and around the world.
Start by pursuing a bachelor’s degree in a Science-related area and specialize in the fields you are most interested in: microbiology, biochemistry, physiology, or public health. You may even consider fields like medicine, engineering, or scholarship.
Is research is your passion? Consider applying for graduate school so you can pursue your research while learning and earning a graduate degree such as Masters or PhD. With a graduate degree, you can work in any scientific field at a higher level, or pursue a career in a related industry.

If graduate degrees are not something you are interested in, consider a college diploma or certificate in areas like lab technician or research assistant. With the right academic background and qualification, you may find your way into a research team or project that meets your interests!
Where Can I Get Help for my Science Studies?
If you are already in an academic program or are still in secondary school and want to perform as best you can in school to get into a competitive school, you may want to consider hiring a tutor in your area of study. Engineering, health sciences, chemistry, and medicine are all rigorous interdisciplinary fields, involving advanced reading and writing skills - so if you find yourself struggling to keep up in certain classes, it is perfectly normal.

A tutor can help you in your greatest areas of need, whether it is calculus or improving your analysis skills in science courses. You can hire a tutor to help explain new concepts, help prepare you for tests and quizzes, or to help you get through your course readings.
Finding the right tutor is easy with Superprof Canada. Superprof is a site that connects students with tutors across different fields. You can use the search tool on the site to find tutors near you or that can work with you virtually.
Summing it Up
The story of insulin, pablum, the Experimental Lakes Area, and the Canadarm are ones of science innovation and ingenuity. Insulin changed diabetes treatment forever, pablum greatly improved the mortality rates of infants, Schindler’s research changed the face of environmental policy, and The Canadarm played a key role in advancing space exploration and research.
The minds behind these great inventions largely remain an inspiration to students of science across Canada.
Who knows, maybe pursuing a career in engineering and science will lead you to become the next great Canadian innovator!
Summarize with AI: